Flow
A flow is an overlay that is displayed before the user attempts an exercise level. The flow should typically contain an overview description of the level with some images, quizzes, and/or interactive canvas.
Use the flow structure below to build flow levels:
- Starts with some historical or general knowledge about the topic
- Have a clear description of the topic
- Description should be like a lesson with as much as possible information. It should not be brief.
- See the Tags section below for instructions on how to use tags when building the topic description.
- Always have programming language-specific content (details are explained in section below (Other Tags)) if needed
- An example and explanation should be for each programming language if needed
- Should not have solution code or such for the given topic
- Include at least 2 quiz questions based on the theory provided in the level
- Use the Quiz Format below (see section "Quiz" and "Tags" below)
- After the last quiz have the lines below:
After Last Quiz
1 2 | |
- Keep the flow easy to read, logically structured, and visually clear
- Avoid overly technical language unless needed
- Structure all levels consistently
Tags
Levels
Flows need to be separated for different levels, so that each level has it's own flow.
To write a flow specific to a level the [level?] tag is used - where ? is the level number starting at 1.
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
This is shown during the flow for Level 1.
This is shown during the flow for Level 2.
Warning
The [level?] tags cannot share a row with anything else, not even other [level?] tags or their own content.
Continue and Coding Buttons
There are two predefined buttons that can be included for the user to press to continue inside the flow or exit it.
The [continue] button is a self closing tag that does not take any content.
It defined the end of a segment within the flow so that everything below it is hidden until the user presses the button.
The [coding] button is used as a final button in the flow for the user to exit the flow and go back to the coding editor.
It takes a body which is the button's text.
Warning
It is not possible to have any continue/coding buttons inside language tags (ex. [english][/english]).
Warning
[continue] and [coding] tags cannot share a row with anything else.
Quiz
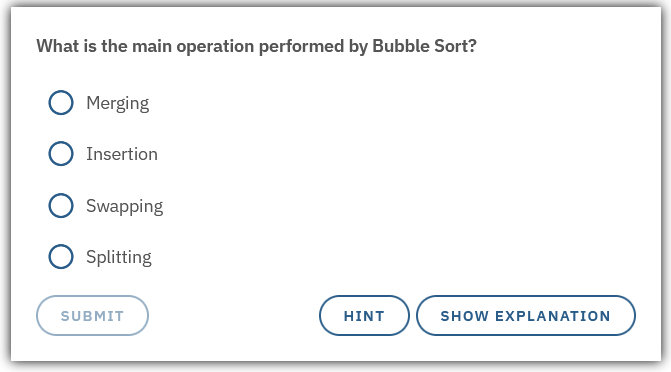
A quiz is a question/answer section that the user can interact with and get either right or wrong.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
quiz |
The main wrapping tag |
question |
The question that is prompted to the user |
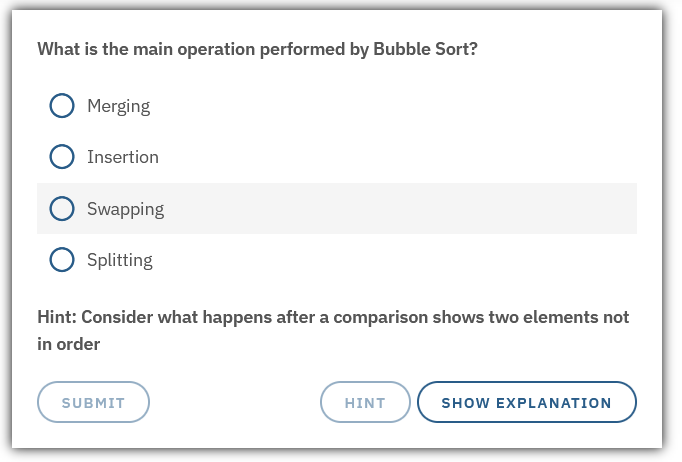
hint |
A hint to the user that can help it if needed |
explanation |
A more detailed explanation of the question's context |
option-correct |
The correct answer to the quiz |
option |
An incorrect answer to the quiz |
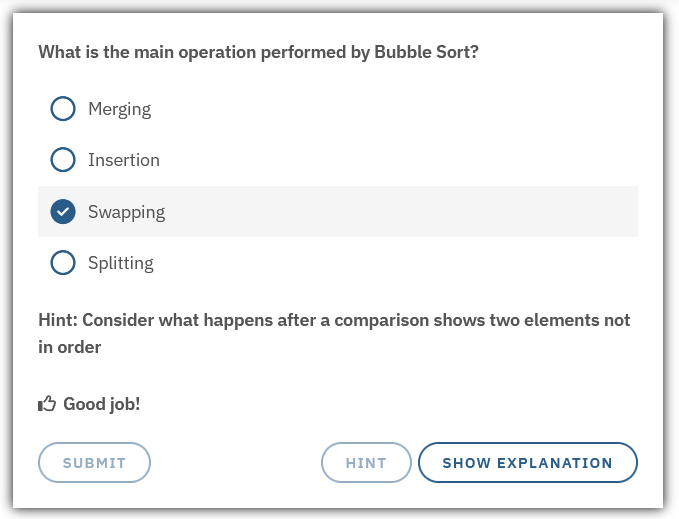
feedback-correct |
The text that is shown to the user if it answers correctly |
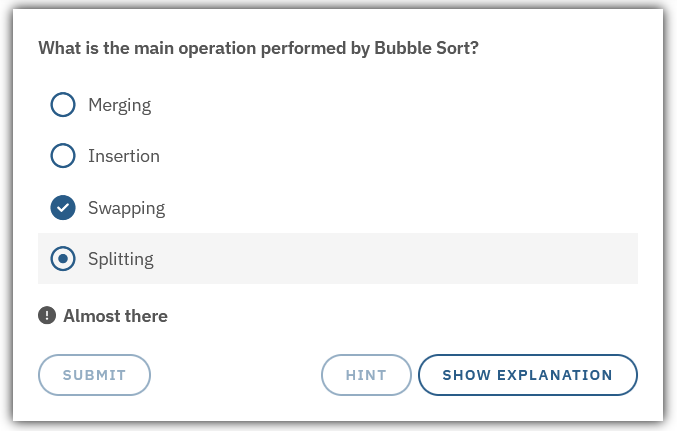
feedback-incorrect |
The text that is shown to the user if it answers incorrectly |
Tags
Warning
All tags are required, but if for example [hint] or [explanation] are left empty they will not render in the flow.
Quiz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
A [continue] or [coding] tag is often needed after the quiz.
Interact
You can add a canvas from one of the levels in a flow.
This can be done using the [interact-?] tag - where ? is the level number starting at 1.
Interact tag
1 | |
Warning
A [continue] tag is needed before and after the interact tag.
Other tags
Several other tags which work in the Description are also supported in the flow, such as:
-
Language tags, e.g.
[swedish]and[english] -
Programming language tags, e.g.
[python]and[c|cpp] -
Switches with default, for example:
Switch with default
1 2 3 4 5 | |
"is" or "==" depending on what you are comparing
===
===
==
- Translation tables, e.g.
Translation table, hello
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
*hello in our flow, it will be rendered as something different depending on which language you are using.
HELLO!!!!
_h_e_l_l_o_
_h_e_l_l_o_
h e l l o . . .
Translation table, programming language
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | |
*language in the flow it will show as the language the user is using:
C
C#
C++
Go
Java
Kotlin
JavaScript
TypeScript
PHP
Python
Ruby
Rust
Scala
the programming language at hand